Embarking on an exploration of the Anatomy of the Constitution Worksheet, this discourse delves into the intricate structure, principles, and historical context that have shaped the foundation of American governance. As we dissect each component, we uncover the significance of the Preamble, the Articles, and the Amendments that have molded the Constitution into a living document.
Delving deeper, we examine the fundamental principles enshrined within the Constitution, including federalism and the separation of powers. We elucidate the concept of checks and balances, highlighting its role in maintaining equilibrium. Furthermore, we explore the Bill of Rights and its profound impact on safeguarding individual freedoms.
Structure of the Constitution: Anatomy Of The Constitution Worksheet

The United States Constitution is the supreme law of the land, establishing the framework for the federal government and safeguarding the fundamental rights of citizens. Its structure reflects the careful balance of power among the different branches of government and the enduring principles that have shaped American democracy.
The Preamble
The Preamble is the opening statement of the Constitution, declaring its purpose and fundamental principles. It sets forth the intent to “form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity.”
The Articles of the Constitution
The Constitution is divided into seven articles, each addressing a specific aspect of the government’s structure and powers.
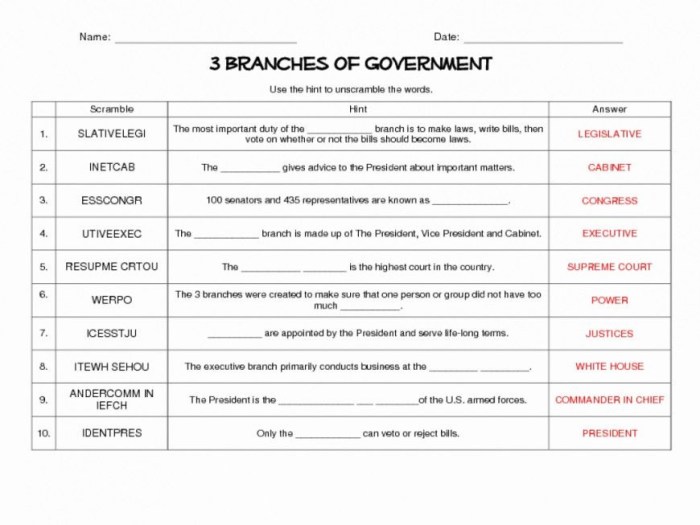
- Article I: Legislative Branch
Establishes the Congress, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives, and defines its powers, including the power to make laws, declare war, and raise taxes.
- Article II: Executive Branch
Creates the office of the President and Artikels the President’s powers and responsibilities, including the power to veto laws, appoint federal officials, and serve as Commander-in-Chief.
- Article III: Judicial Branch
Establishes the Supreme Court and defines the structure and powers of the federal judiciary, including the power to interpret laws and declare them unconstitutional.
- Article IV: Relations Among States
Ensures full faith and credit among the states, regulates interstate commerce, and provides for the admission of new states.
- Article V: Amendment Process
Artikels the process for amending the Constitution, which requires a two-thirds vote of Congress and ratification by three-fourths of the states.
- Article VI: Supremacy Clause
Establishes the Constitution as the supreme law of the land, binding on all state and federal governments and their officials.
- Article VII: Ratification
Sets forth the conditions for ratifying the Constitution, which required the approval of at least nine of the thirteen original states.
Amendments
The Constitution has been amended 27 times since its ratification in 1789. Amendments have played a crucial role in shaping the Constitution, expanding its scope, and addressing changing societal needs.
- Bill of Rights (Amendments 1-10)– Protects individual freedoms, including freedom of speech, religion, and the right to bear arms.
- Reconstruction Amendments (Amendments 13-15)– Abolished slavery, granted citizenship to African Americans, and guaranteed due process and equal protection under the law.
- Progressive Era Amendments (Amendments 16-19)– Introduced the income tax, granted women the right to vote, and established prohibition.
- New Deal Amendments (Amendments 20-22)– Limited presidential terms, repealed prohibition, and extended the right to vote to 18-year-olds.
Principles and Concepts
The United States Constitution is a document that Artikels the principles and structure of the federal government. It establishes the basic framework for how the government operates and defines the relationship between the federal government and the states. The Constitution is based on a number of fundamental principles, including federalism, separation of powers, and checks and balances.
Federalism
Federalism is a system of government in which power is divided between a central government and regional governments. In the United States, the federal government is responsible for matters that affect the entire nation, such as foreign policy, defense, and interstate commerce.
The states are responsible for matters that affect their own citizens, such as education, law enforcement, and public health.
Separation of Powers
Separation of powers is a system of government in which the powers of government are divided among different branches. In the United States, the three branches of government are the legislative branch, the executive branch, and the judicial branch. The legislative branch makes the laws, the executive branch enforces the laws, and the judicial branch interprets the laws.
Checks and Balances
Checks and balances is a system of government in which each branch of government has the ability to check the power of the other branches. This helps to prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful. For example, the legislative branch can override a veto by the executive branch, and the judicial branch can declare laws passed by the legislative branch to be unconstitutional.
Bill of Rights
The Bill of Rights is a collection of ten amendments to the Constitution that guarantee certain individual freedoms. These freedoms include the right to free speech, the right to bear arms, and the right to a fair trial. The Bill of Rights is one of the most important parts of the Constitution, and it has helped to protect the rights of individuals for over 200 years.
Historical Context and Influences
The drafting of the Constitution was a culmination of historical events and intellectual influences that shaped the American political landscape. The American Revolution, the Declaration of Independence, and the Articles of Confederation were pivotal in setting the stage for the creation of a new constitutional framework.
Enlightenment thinkers, such as John Locke and Montesquieu, provided the philosophical underpinnings for the Constitution. Their ideas on natural rights, limited government, and the separation of powers influenced the structure and principles of the document.
Drafting and Debates, Anatomy of the constitution worksheet
The Constitutional Convention was held in Philadelphia in 1787, bringing together delegates from the 13 states to address the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation. The debates and compromises that took place during the convention shaped the final document.
- The Great Compromise:This compromise resolved the issue of representation between large and small states by creating a bicameral legislature, with the Senate representing states equally and the House of Representatives based on population.
- The Three-Fifths Compromise:This compromise counted enslaved people as three-fifths of a free person for purposes of representation and taxation.
- The Electoral College:This compromise established an indirect method for electing the president, which was seen as a safeguard against popular passions.
Impact and Legacy
The United States Constitution has profoundly shaped the nation’s history and society. It has served as the foundation for the country’s legal system, establishing a framework for government and protecting individual rights and liberties.
The Constitution has been interpreted and adapted over time to meet the changing needs of the nation. This has been accomplished through amendments, Supreme Court rulings, and the evolution of legal doctrines. These adaptations have ensured that the Constitution remains a living document, capable of addressing new challenges and safeguarding the fundamental principles of American democracy.
Landmark Supreme Court Cases
The Supreme Court has played a pivotal role in shaping constitutional law. Landmark cases such as Marbury v. Madison(1803), Dred Scott v. Sandford(1857), Brown v. Board of Education(1954), and Roe v. Wade(1973) have had a profound impact on the interpretation and application of the Constitution.
- Marbury v. Madisonestablished the principle of judicial review, giving the Supreme Court the authority to declare laws unconstitutional.
- Dred Scott v. Sandforddenied citizenship to African Americans and upheld the legality of slavery, a decision that contributed to the outbreak of the Civil War.
- Brown v. Board of Educationoverturned the doctrine of “separate but equal” and declared racial segregation in public schools unconstitutional.
- Roe v. Wadeestablished a woman’s right to choose to have an abortion, a decision that remains controversial and has been the subject of ongoing legal challenges.
Comparative Analysis
The US Constitution stands as a seminal document in constitutional history, influencing the development of numerous constitutions worldwide. By comparing it to other notable constitutions, we gain insights into its unique features, principles, and historical contexts.
Structurally, the US Constitution exhibits a federalist system, dividing power between the national and state governments. This contrasts with unitary systems, where power is concentrated at the national level. Moreover, the US Constitution establishes a system of checks and balances, distributing power among different branches of government to prevent tyranny.
Similarities and Differences
- Principles:Many constitutions share fundamental principles such as the rule of law, individual rights, and democratic governance. However, the specific articulation and interpretation of these principles may vary.
- Historical Contexts:The historical contexts that shaped the US Constitution, such as the Enlightenment and the American Revolution, also influenced the development of other constitutions. However, local circumstances and cultural norms have led to distinct constitutional frameworks.
Influence of the US Constitution
The US Constitution has had a profound influence on the development of other constitutions. Its federalist structure, system of checks and balances, and Bill of Rights have been adopted or adapted in numerous countries. For example, the Canadian Constitution incorporates the principles of federalism and individual rights enshrined in the US Constitution.
Helpful Answers
What is the significance of the Preamble to the Constitution?
The Preamble sets forth the fundamental purposes and principles of the Constitution, including establishing a more perfect union, securing the blessings of liberty, and promoting the general welfare.
How many Articles are there in the Constitution?
There are seven Articles in the Constitution, each addressing a specific aspect of the government’s structure and powers.
What is the role of Amendments in the Constitution?
Amendments are changes to the Constitution that have been ratified through a specific process. They have played a crucial role in adapting the Constitution to changing circumstances and societal values.