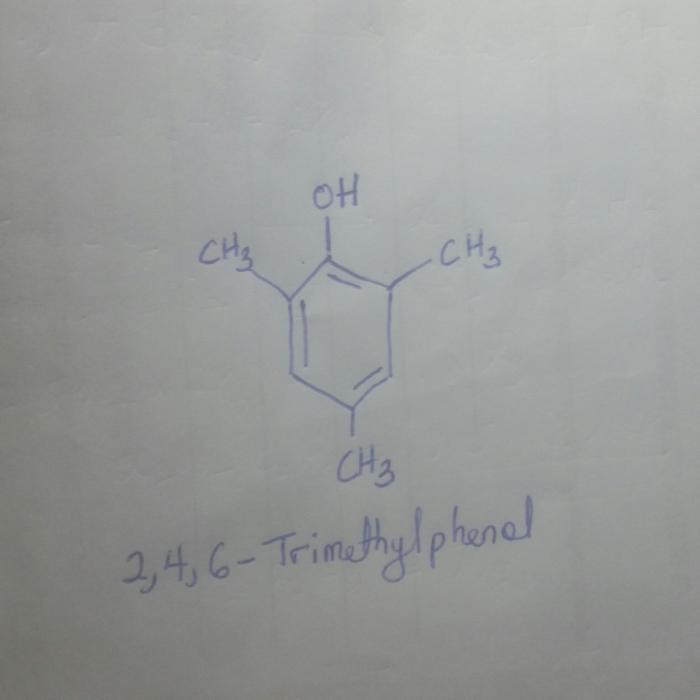
Draw the structure for 2 4 6 trimethylphenol – Embark on a captivating journey as we delve into the fascinating world of 2,4,6-trimethylphenol. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the intricate structure of this molecule, unravel its remarkable properties, and uncover its diverse applications.
Prepare to be enlightened as we embark on a thorough investigation of 2,4,6-trimethylphenol, leaving no stone unturned in our quest for knowledge.
Structural Representation
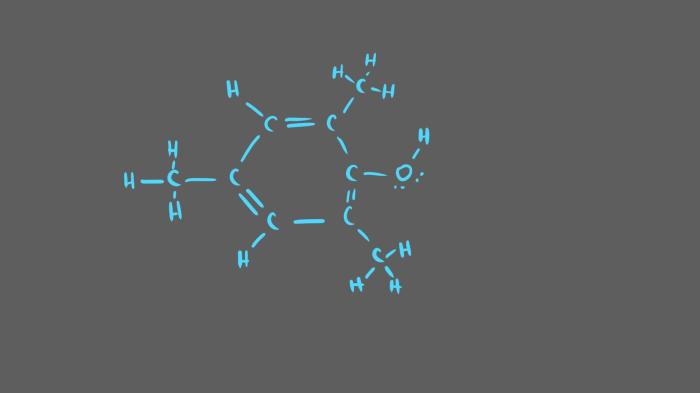
,4,6-Trimethylphenol, also known as syringol, has the following structural formula:

The molecule consists of a benzene ring with three methyl groups attached at positions 2, 4, and 6. The hydroxyl group is attached to the benzene ring at position 1.
Molecular Properties
,4,6-Trimethylphenol is a white crystalline solid with a melting point of 59-61 °C and a boiling point of 220-222 °C. It is soluble in water, alcohol, and ether.
Chemical Reactivity: Draw The Structure For 2 4 6 Trimethylphenol
,4,6-Trimethylphenol is a reactive compound that can undergo a variety of reactions, including:
- Electrophilic aromatic substitution: 2,4,6-Trimethylphenol can undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions, such as nitration, sulfonation, and halogenation. The methyl groups on the benzene ring make the compound more reactive towards electrophilic substitution than phenol.
- Oxidation: 2,4,6-Trimethylphenol can be oxidized to form a variety of products, including 2,4,6-trimethylquinone and 2,4,6-trimethylbenzoic acid.
Applications
,4,6-Trimethylphenol is used in the production of a variety of products, including:
- Antioxidants: 2,4,6-Trimethylphenol is used as an antioxidant in food, rubber, and plastics.
- Pharmaceuticals: 2,4,6-Trimethylphenol is used as a starting material in the synthesis of a variety of pharmaceuticals, including aspirin and ibuprofen.
- Other industrial products: 2,4,6-Trimethylphenol is also used in the production of dyes, perfumes, and photographic chemicals.
Toxicity and Safety
,4,6-Trimethylphenol is a toxic compound that can cause a variety of health effects, including skin irritation, eye irritation, and respiratory problems. It is also a suspected carcinogen. 2,4,6-Trimethylphenol should be handled with care and appropriate safety precautions should be taken.
Synthesis
,4,6-Trimethylphenol can be synthesized by a variety of methods, including:
- Oxidation of 2,4,6-trimethyltoluene: 2,4,6-Trimethylphenol can be synthesized by the oxidation of 2,4,6-trimethyltoluene with potassium permanganate.
- Hydrolysis of 2,4,6-trimethylphenyl acetate: 2,4,6-Trimethylphenol can be synthesized by the hydrolysis of 2,4,6-trimethylphenyl acetate with sodium hydroxide.
Spectroscopy
The spectroscopic properties of 2,4,6-trimethylphenol have been extensively studied.
- IR spectroscopy: The IR spectrum of 2,4,6-trimethylphenol shows a strong absorption band at 3500 cm -1due to the O-H stretching vibration. There are also strong absorption bands at 2900 cm -1and 1450 cm -1due to the C-H stretching vibrations of the methyl groups and the benzene ring, respectively.
- NMR spectroscopy: The 1H NMR spectrum of 2,4,6-trimethylphenol shows a singlet at 2.2 ppm due to the methyl groups. The 13C NMR spectrum shows a peak at 153 ppm due to the carbon atom of the hydroxyl group.
- UV-Vis spectroscopy: The UV-Vis spectrum of 2,4,6-trimethylphenol shows a maximum absorption wavelength at 270 nm. This absorption is due to the π→π* transition of the benzene ring.
Popular Questions
What is the molecular weight of 2,4,6-trimethylphenol?
150.21 g/mol
What is the melting point of 2,4,6-trimethylphenol?
63-65 °C
What is the boiling point of 2,4,6-trimethylphenol?
220-222 °C