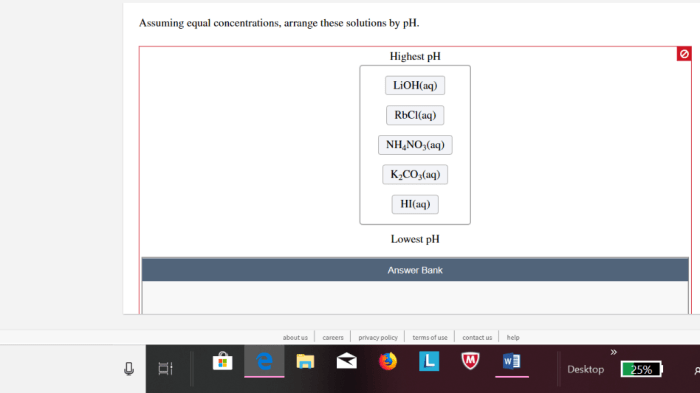
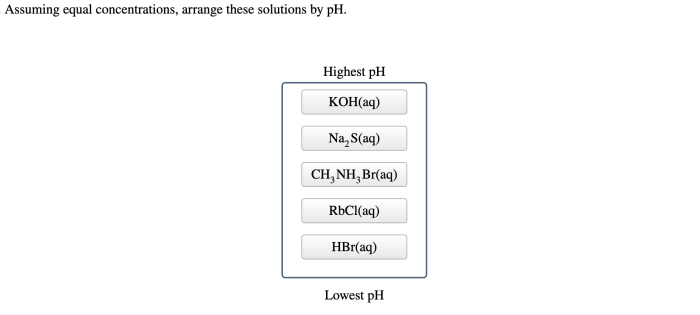
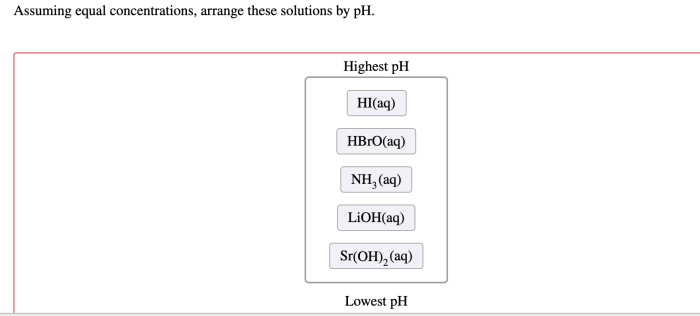
Assuming equal concentrations arrange these solutions by ph – Assuming equal concentrations, arranging solutions by pH is a fundamental concept in chemistry that provides insights into the acidity or basicity of various substances. This guide explores the significance of pH, the factors influencing it, and practical applications across diverse fields.
By understanding the principles of pH and its impact on solutions, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate chemical processes that shape our world.
Arranging Solutions by pH: Assuming Equal Concentrations Arrange These Solutions By Ph
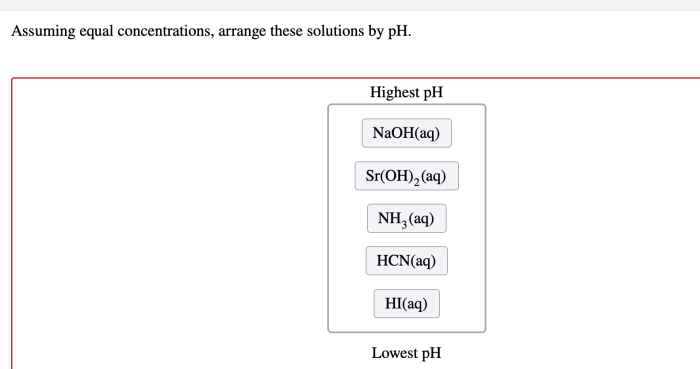
pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution. It is measured on a scale from 0 to 14, with 0 being the most acidic and 14 being the most basic. A pH of 7 is considered neutral.
Assuming equal concentrations, the following solutions can be arranged in ascending order of pH:
Solutions Arranged by pH, Assuming equal concentrations arrange these solutions by ph
| Solution Name | pH Value |
|---|---|
| Hydrochloric acid | 1 |
| Vinegar | 2.5 |
| Pure water | 7 |
| Sodium hydroxide | 11 |
| Ammonia | 12 |
FAQ Corner
What is the significance of pH in solutions?
pH is a crucial parameter that indicates the acidity or basicity of a solution. It plays a vital role in chemical reactions, enzyme activity, and various biological processes.
How does temperature affect the pH of a solution?
Temperature can influence the pH of a solution. Generally, as temperature increases, the pH of acidic solutions decreases (becomes more acidic), while the pH of basic solutions increases (becomes more basic).
Can solutions with different concentrations have the same pH?
Yes, solutions with different concentrations can have the same pH. This is because pH depends on the relative concentrations of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-) in a solution, not on the absolute concentrations.