Essentials of human anatomy and physiology 13th edition – Welcome to the captivating world of human anatomy and physiology, where the intricate workings of the human body are illuminated through the Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 13th Edition. This comprehensive textbook embarks on a journey of discovery, unraveling the secrets of our physical form and its remarkable functions.
Delving into the fundamental principles of human biology, this edition provides a thorough understanding of the body’s organization, from the microscopic level of cells to the macroscopic level of organ systems. With its engaging narrative and up-to-date content, Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 13th Edition empowers students to grasp the complexities of the human body and its intricate interplay of structures and processes.
Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Human anatomy is the study of the structure of the human body, while human physiology is the study of the function of the human body. Together, anatomy and physiology provide a comprehensive understanding of how the human body works. Studying human anatomy and physiology is important for a variety of reasons, including:
- Understanding the human body is essential for diagnosing and treating diseases.
- Understanding the human body can help us develop new drugs and treatments.
- Understanding the human body can help us improve our overall health and well-being.
The human body is organized into a hierarchy of levels, from the smallest to the largest. The smallest level is the atomic level, which includes atoms and molecules. The next level is the cellular level, which includes cells. The next level is the tissue level, which includes tissues.
The next level is the organ level, which includes organs. The next level is the system level, which includes systems. The largest level is the organismal level, which includes the entire organism.
Basic Chemistry of Life
The human body is composed of atoms and molecules. Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter, and they are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Molecules are formed when two or more atoms bond together. The chemical bonds that hold atoms together are formed by the sharing or transfer of electrons.
Water is the most abundant molecule in the human body. It is essential for life, and it plays a role in a variety of bodily functions, including temperature regulation, nutrient transport, and waste removal.
pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. The pH of the human body is carefully regulated, and it is essential for the proper functioning of cells.
Cells: The Basic Unit of Life

Cells are the basic unit of life. They are the smallest units that can carry out all the functions of life. Cells are classified into two main types: prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are simpler than eukaryotic cells, and they do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles.
Eukaryotic cells are more complex than prokaryotic cells, and they have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
Cells divide by a process called cell division. Cell division is essential for growth, repair, and reproduction.
There are many different types of cells in the human body. Each type of cell has a specific structure and function.
Tissues: Essentials Of Human Anatomy And Physiology 13th Edition

Tissues are groups of cells that have a similar structure and function. There are four main types of tissues in the human body: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue.
Epithelial tissue covers the surfaces of the body and lines the cavities of the body. It protects the body from the environment and helps to regulate the passage of substances into and out of the body.
Connective tissue supports and connects the other tissues of the body. It also stores energy and provides insulation.
Muscle tissue allows the body to move. It is found in the muscles of the skeleton, the heart, and the digestive system.
Nervous tissue controls the body’s activities. It is found in the brain, the spinal cord, and the nerves.
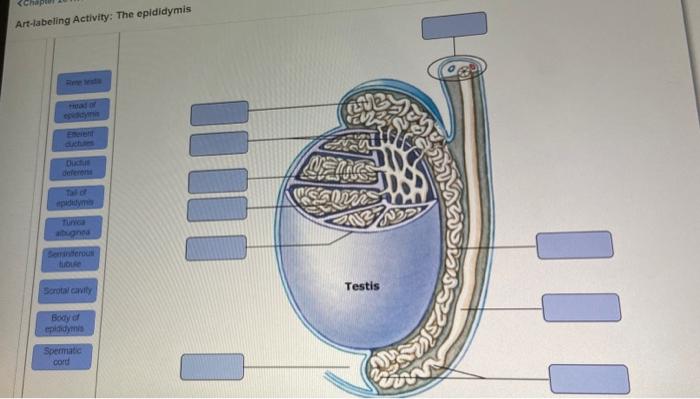
Integumentary System
The integumentary system is the organ system that protects the body from the environment. It consists of the skin, hair, nails, and sweat glands.
The skin is the largest organ of the body. It protects the body from the environment, helps to regulate body temperature, and stores water and fat.
Hair helps to insulate the body and protect it from the sun.
Nails protect the tips of the fingers and toes.
Sweat glands help to regulate body temperature by releasing sweat.
Key Questions Answered
What is the significance of studying human anatomy and physiology?
Understanding human anatomy and physiology is crucial for comprehending the structure and function of the human body, which is essential for healthcare professionals, researchers, and individuals seeking a holistic understanding of their own biology.
How does Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 13th Edition differ from previous editions?
The 13th edition features updated content, improved illustrations, and enhanced pedagogical tools to facilitate learning. It incorporates the latest research findings and advancements in the field of human anatomy and physiology.
Is this textbook suitable for students with no prior knowledge of anatomy and physiology?
Yes, Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 13th Edition is designed to be accessible to students with varying backgrounds. It provides a comprehensive introduction to the subject, making it suitable for both beginners and those seeking to refresh their knowledge.